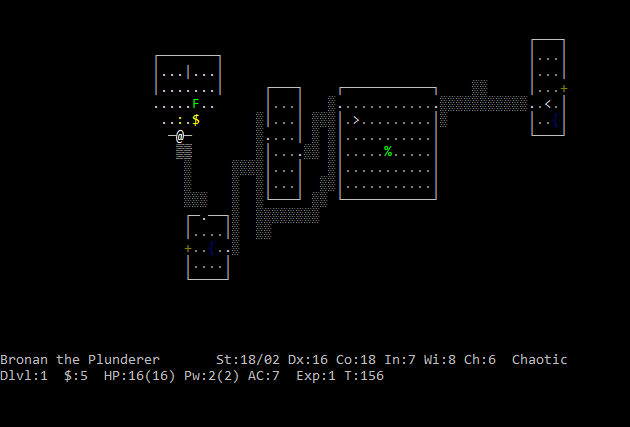
Nostalgia and old-school gameplay philosophy dictate the complex conventions of roguelikes
Mark R. Johnson writes in his article “The Use of ASCII Graphics in Roguelikes: Aesthetic Nostalgia and Semiotic Difference”, published in Games and Culture, about how the old-school graphics used in roguelike games are special in the sense that they all have unique, game-specific meanings, but still tie the games to the nostalgic tradition.
The term ‘roguelike’ refers to games imitating the style of Rogue, a game released in 1980, that introduces complex, randomized levels, turn-based combat and permadeath within an American Standard Code for Information Interchange (ASCII) user-interface. While Rogue used the rudimentary graphics to enable playing on various platforms, later roguelikes, such as NetHack or Dungeon Crawl, have adopted the style to indicate continued tradition of old-school gameplay philosophy. Many players feel that focusing on graphics takes away from gameplay and gives less room for player imagination. By imitating Rogue, these games aim to promise a similar gameplay experience and an emphasis on actual gameplay.
Video games rely on existing genre conventions to communicate meanings, since players will automatically expect certain things from certain creatures, for example. However, almost every ASCII game presents game objects, such as enemies, in a unique combination of letter sizes and colours. Learning the logic of one roguelike only means more difficulty in trying to decipher another one, as players will have to unlearn the glyphs of the previous game.
Roguelike players might know that the letter “f” may refer to a feline class of enemies, or that “W” may be used to denote wraiths and wraith-like creatures, but they have no way of guessing which conventions are used in which games without memorizing them. To further complicate matters, there are rare occasions in which, for example, “q” is used as a continuation of the draconian class represented by “p” because it is the mirror image of the same letter. One thing most roguelikes have in common is that the choice of letter is usually higher in hierarchy than the colour, which in that case simply differentiates specific monsters within the class denoted by the letter.
ASCII roguelikes are built upon a curious combination of unintuitive gameplay and appeal to nostalgia, but the distinct style instantly tells the player what to expect from these games. They follow traditions to stay true to their predecessors and separate them from contemporary games.
Author: Mark R. Johnson
Published in: Games and Culture volume 12 issue 2, March 1, 2017; originally published May 17, 2015
Original article: http://journals.sagepub.com/doi/abs/10.1177/1555412015585884?journalCode=gaca
You might also like
More from Game Research Highlights
How do you want to do this? – A look into the therapeutic uses of role-playing games
Can playing RPGs contribute positively to your wellbeing? A recent study aims to find out how RPGs are being used …
Eldritch horrors and tentacles – Defining what “Lovecraftian” is in games
H.P. Lovecrafts legacy lives today in the shared world of Cthulhu Mythos and its iconic monsters. Prema Arasu defines the …
Are Souls Games the Contemporary Myths?
Dom Ford’s Approaching FromSoftware’s Souls Games as Myth reveals the Souls series as a modern mythology where gods fall, desires …