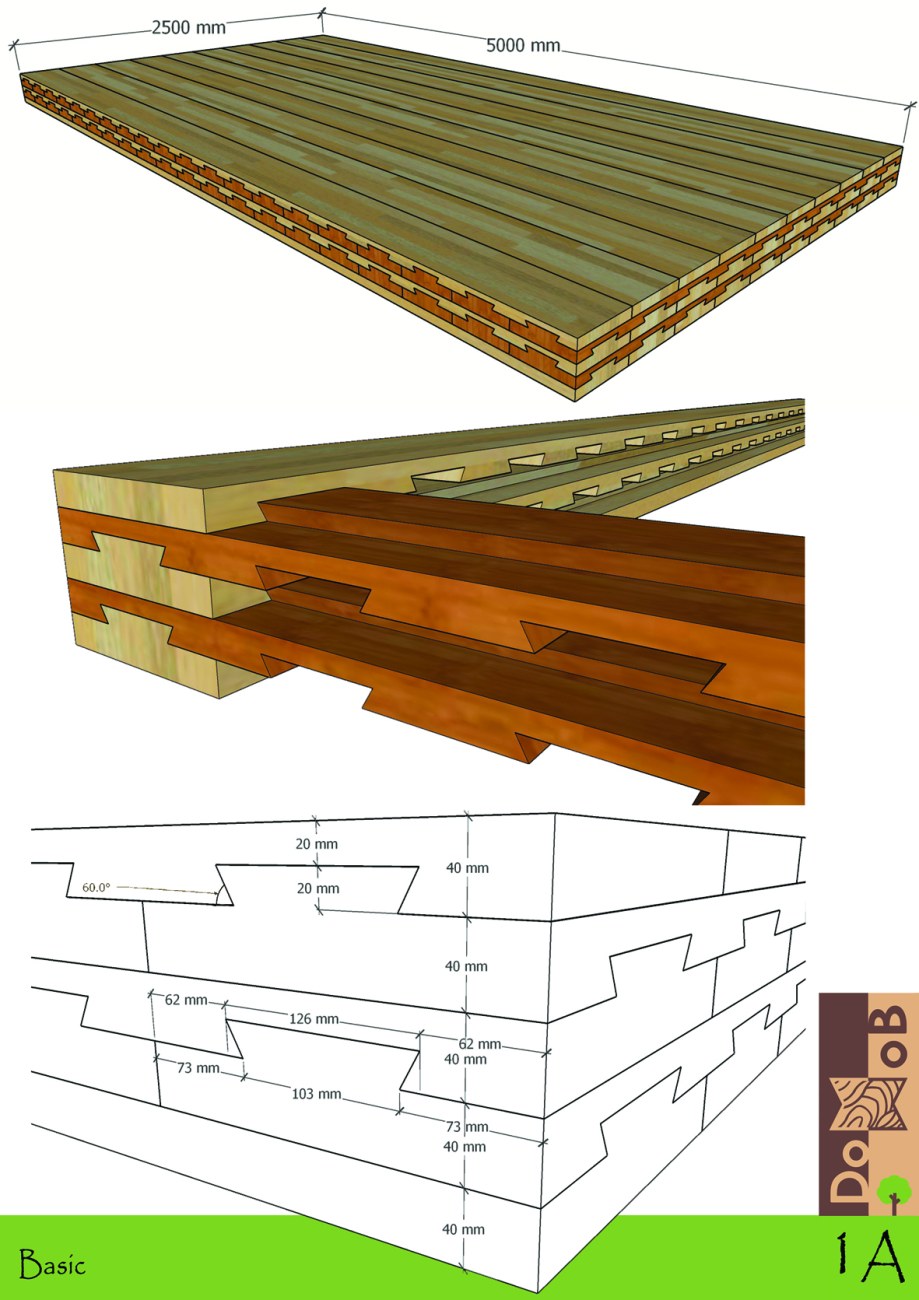
Dovetailed massive wood board elements (DMWBEs) are based on one of the oldest traditional techniques used in joinery. Although numerous studies have been conducted on the technological, ecological, social and economic aspects of engineered wood products (EWPs) in the construction sector, none has evaluated the technical performance of DMWBEs in multi-story buildings. The EU-funded DoMWoB project will develop DMWBEs for multi-story buildings as a replacement of conventional EWPs through multidisciplinary collaboration, involving architecture, structure, and building physics. The initiative will design, build, test, and conduct market research on DMWBEs and promote the competitiveness of Finnish large-scale industrial wooden construction and circular economy opportunities, as well as sustainable development in support of Europe's bio-economy climate policy.


Background
As a result of global urbanization, the trend to build more vertical cities has been becoming more suitable for changing lifestyles, economics, and urbanization. Even Scandinavian cities could be now on the cusp of their own high-rise revolution. Furthermore, building higher has been gradually gaining popularity as in the cases of numerous tall towers e.g. 180m Trigoni Tower 1, Finland.
As a renewable material, wood is unquestionably ecological and environmentally friendly: one cubic meter of growing wood can bind about one ton of CO2 from the atmosphere, the mass of wood is about 500 kg/m3, and about half of this mass is carbon = 250 kg/m3. Forests are carbon sinks and wood products are carbon storage. Therefore, it is reasonable to use so much massive wood as possible particularly in multi-story construction.
Moreover, thanks to its considerably lower carbon footprint and potential cost-effectiveness compared to traditional materials such as reinforced concrete and steel, and numerous positive impacts on the environment, accompanied by its technological advances; wood, in the form of engineered wood products (EWPs), has come back to break into the multi-story building, and even tall building, utilization after more than a century.
Prior to the early 1990s, most of the wooden buildings in European countries were limited to 1 or 2-story due to fire performance regulation restriction, while in recent years, thanks to the national building regulations shifting from being prescriptive to functional or performance-based, multi-story wooden construction has been gaining acceptance in European countries. Concordantly, a wide variety of EWPs is currently available on the market. They are gradually replacing conventional building materials for multi-story construction.
In this sense, the multi-story wooden buildings have been a new promising industry with a high capacity for supporting the bio-economy and technologically refurbishing construction sector. They can contribute to social well-being both within primary production and within wood-based value chains. In this industry, as a growing market in Europe, EWPs e.g. cross-laminated timber (CLT), glue-laminated timber (Glulam), laminated veneer lumber (LVL), Massiv-Holz-Mauer® (MHM) have had an important position with the production capacity of more than 5 million cubic meter/year.
In EWPs, adhesives play an essential role particularly by helping save wood, making the structure light and robust, and moderating the expansion and contraction due to the inherent moisture. However, although there are advantages above associated with EWPs, the use of adhesives causes some concerns about their sustainability, recyclability, and broader environmental impact. More in particular, because of toxic gas emissions resulting from their petroleum-based contents, the dominant use of adhesives has adverse effects on the environment e.g. climate change, air pollution, and human health.
Thus, there is still room for a solution that is solid and completely pure wood enabling as healthy indoor air as possible (adhesive-&metal-connectors-free) dovetailed massive wood board elements (DMWBE) based on one of the oldest joining methods used traditionally.
Goal
The aim of this research is to promote the competitiveness of Finnish large-scale industrial wooden construction at the local level and to create higher value-added circular economy opportunities in support of European climate policy as part of the bio-economy and sustainable development. To achieve this goal, DMWBE for multi-story buildings to the global market as a replacement of conventional EWPs e.g. cross-laminated timber, glue-laminated timber will be developed by enabling the confidence of its technical performance and suitability within the interdisciplinary collaborations among architecture, structure, and building physics. The following main objectives have been identified: Designing, building, and testing, and finally conducting market research of DMWBE in multi-story, maybe even tall, construction.
Funding source

This project has received funding from the European Union’s Horizon 2020 research and innovation programme under the Marie Skłodowska-Curie grant agreement No [101024593].
Total costs (including non-EU funded): 202 680.96 EUR

This project has also received funding (60 000 EUR) from the Marjatta and Eino Kolli Foundation for funding the technical performance tests including fire safety, structural, moisture transfer resistance & air-tightness, and sound insulation.
People
Emre Ilgin
Postdoctoral Research Fellow Emre Ilgin
Emre IlginPublications
Ilgın, H.E.; Karjalainen, M. Preliminary Design Proposals for Dovetail Wood Board Elements in Multi-Story Building Construction. Architecture 2021, 1, 56-68.
https://doi.org/10.3390/architecture1010006
Ilgın, H.E., Karjalainen, M., Koponen, O. Review of the current state-of-the-art of dovetail massive wood elements, Engineered Wood Products for Construction, IntechOpen, 2021, DOI: 10.5772/intechopen.99090, ISBN 978-1-83962-772-9
https://www.intechopen.com/online-first/77634
Ilgın, H.E., Karjalainen, M., Koponen, O. Dovetail Massive Wood Board Elements for Multi-Story Buildings, LIVENARCH VII Livable Environments & Architecture 7th International Congress OTHER ARCHITECT/URE(S), September 28-30, 2021, Trabzon, Turkey, Volume I, p. 47-60.
Ilgın, H.E., Karjalainen, M., Koponen, O. Various geometric configuration proposals for dovetail wooden horizontal structural members in multi-story building construction, Engineered Wood Products for Construction, IntechOpen, 2021 DOI: 10.5772/intechopen.101725, ISBN 978-1-83962-772-9
Ilgın, H.E., Karjalainen, M., Koponen, O., Soikkeli, A. A Study on Contractors’ Perception of Using Wood for Construction, Engineered Wood Products for Construction, IntechOpen, 2022 DOI: 10.5772/intechopen.103168, ISBN 978-1-83962-772-9
Presentations
by Olli-Paavo Koponen, Professor of Architectural History; Markku Karjalainen, Professor of Architectural Construction, and Emre Ilgın, Dr, Architect, Post-doc researcher

Our first dovetailed massive wood board element is ready for fire resistance testing!

Installation of the first layer

Fire performance tests for Dovetail and CLT boards /// Char rates about 0.92 mm/min (CLT) & 0.70 mm/min (Dovetail) for second lamella layer /// Dovetail performed significantly better than CLT (Typically, acceptable char rates for timber are about 0.50 mm/min for hardwoods and 0.65 mm/min for softwoods)

Airborne sound insulation test for Dovetail and CLT boards /// Rw (Dovetail) - 43 dB > Rw (CLT) - 40 dB /// Dovetail performed significantly better than CLT.

Our dowelled dovetail wooden board is ready for the structural bending test.